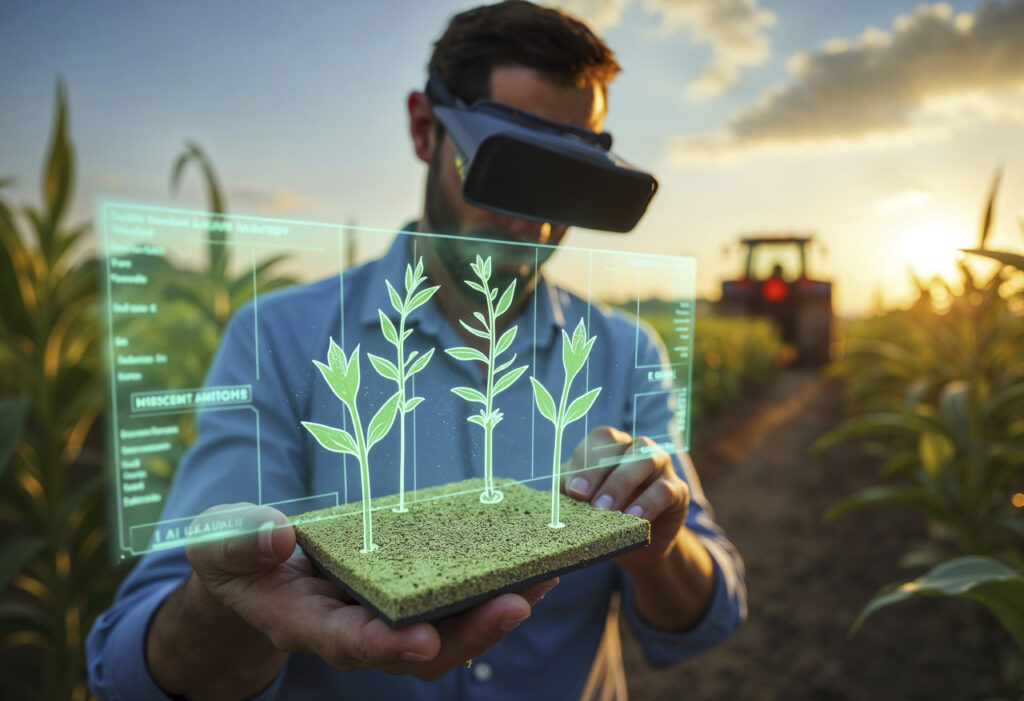
Agriculture has always been the backbone of human civilization, but in today’s rapidly evolving world, traditional farming methods are no longer sufficient to meet the growing demand for food, sustainability, and efficiency. This is where Smart Agriculture, also known as Precision Farming or Digital Agriculture, comes into play. By integrating advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), drones, data analytics, and automation, smart agriculture is revolutionizing the way farmers grow, manage, and distribute crops.
Just as Pune Realty has embraced modern infrastructure and smart living solutions to redefine urban development, the agricultural sector is leveraging innovation to create a more productive, sustainable, and profitable future.
What Is Smart Agriculture?
Smart agriculture refers to the use of advanced digital technologies to enhance farming practices. It focuses on data-driven decision-making to optimize crop yield, reduce resource wastage, and improve overall farm management. Instead of relying solely on experience and manual labor, farmers now have access to real-time data, predictive insights, and automated systems.
This transformation is essential as global challenges such as climate change, population growth, and shrinking arable land demand smarter and more efficient farming solutions.
Key Technologies Driving Smart Agriculture
1. Internet of Things (IoT) in Farming
IoT devices such as soil sensors, weather stations, and smart irrigation systems collect real-time data on soil moisture, temperature, humidity, and nutrient levels. Farmers can monitor their fields remotely and make timely decisions.
For example, smart irrigation systems automatically supply water only when needed, reducing water wastage—a crucial step toward sustainability, much like energy-efficient planning seen in modern Pune Realty developments.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI-powered systems analyze large datasets to predict crop diseases, pest attacks, and optimal harvesting times. Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns that humans might overlook, enabling proactive rather than reactive farming.
AI also supports yield prediction, helping farmers plan storage, transportation, and pricing more effectively.
3. Drones and Aerial Imaging
Agricultural drones are transforming farm monitoring. Equipped with high-resolution cameras and multispectral sensors, drones provide aerial views of crops, allowing farmers to:
- Detect plant stress early
- Identify pest-infested areas
- Monitor crop growth
- Optimize fertilizer application
This targeted approach saves time, reduces costs, and minimizes environmental impact.
4. Smart Machinery and Automation
Automated tractors, robotic harvesters, and smart planting machines are reducing dependence on manual labor. These machines operate with high precision, ensuring uniform planting and harvesting while minimizing errors.
Automation in farming mirrors the rise of smart homes and automated amenities commonly highlighted in Pune Realty residential projects.
5. Big Data and Cloud Computing
Smart agriculture relies heavily on data analytics. Cloud-based platforms store and analyze massive amounts of information collected from farms. Farmers can access insights through mobile apps and dashboards, helping them plan crops, manage risks, and increase profitability.
Data-driven farming also improves traceability, which is increasingly important for food safety and export standards.
Benefits of Smart Agriculture
Increased Productivity and Yield
By using precise data and automated tools, farmers can maximize output while minimizing losses. Early detection of issues ensures healthier crops and better harvests.
Efficient Resource Management
Smart agriculture reduces wastage of water, fertilizers, and pesticides. Precision application ensures that resources are used only where needed, promoting sustainability.
Cost Reduction
While the initial investment may seem high, smart technologies significantly lower long-term operational costs. Reduced labor, optimized input usage, and improved yields contribute to better profit margins.
Environmental Sustainability
Smart farming practices help reduce soil degradation, water pollution, and carbon emissions. Sustainable agriculture aligns with the growing emphasis on eco-friendly development, a trend also gaining momentum in Pune Realty projects.
Climate Resilience
With unpredictable weather patterns, smart agriculture enables farmers to adapt quickly. Weather forecasting tools and climate analytics help mitigate risks caused by droughts, floods, and extreme temperatures.
Challenges in Adopting Smart Agriculture
Despite its benefits, smart agriculture faces certain challenges:
- High initial investment costs
- Limited digital literacy among small-scale farmers
- Inadequate internet connectivity in rural areas
- Data privacy and security concerns
Addressing these challenges requires government support, training programs, and affordable technology solutions.
Government Initiatives and Support
Many governments, including India, are actively promoting digital farming through initiatives such as:
- Subsidies for smart equipment
- Digital soil health cards
- Agri-tech startup support
- Farmer training programs
Such initiatives are creating an ecosystem where technology and agriculture coexist for long-term growth—similar to how infrastructure development boosts the real estate sector, including Pune Realty.
The Future of Smart Agriculture
The future of farming lies in fully integrated ecosystems where AI, robotics, blockchain, and biotechnology work together. Concepts like vertical farming, hydroponics, and smart greenhouses are gaining popularity, especially near urban areas.
As cities expand and urbanization increases, smart agriculture will play a vital role in ensuring food security for growing populations—complementing urban expansion trends seen in regions driven by Pune Realty development.
Most countries, including the Indian government, are encouraging the adoption of digital farming by:
Subsidies for smart devices
Digital soil health cards
Support to agri-tech startups
Farmer training programs
The Future of Smart Agriculture
The future of agriculture is in the development of an integrated system involving AI, robots, blockchain, and biotech solutions. Ideas such as vertical farming, hydroponics, and intelligent greenhouse farming are becoming increasingly popular, especially in urban proximity.
Conclusion
Smart agriculture is not just a technological upgrade; it is a necessity for sustainable and profitable farming in the modern world. By embracing innovation, farmers can overcome traditional limitations, protect natural resources, and secure better livelihoods.