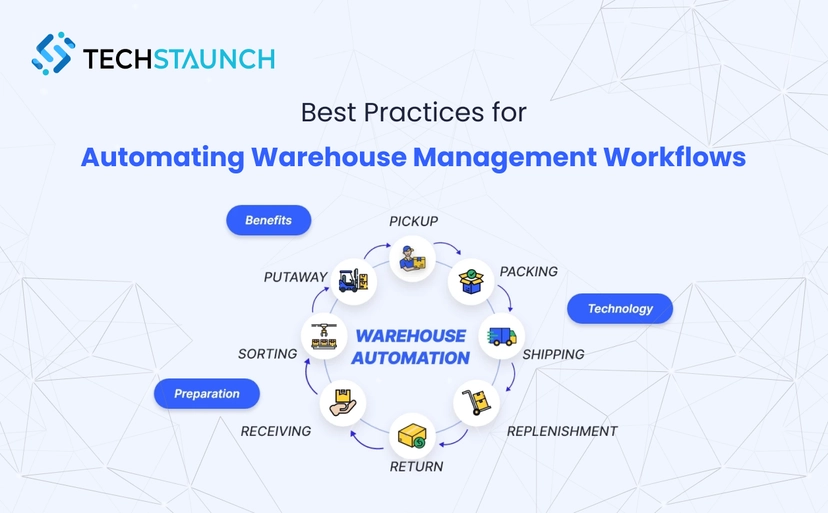
In today’s fast-paced supply chain environment, a well-designed warehouse management workflow isn’t just a nice-to-have — it’s essential for operational excellence and long-term growth. With rising customer expectations, labor shortages, and increasing order complexity, businesses are turning to Automating Warehouse Management Workflows to stay competitive and efficient.
Why Warehouse Management Workflow Matters
A warehouse management workflow defines how goods move from receipt to shipping. It includes steps like inventory tracking, order picking, packing, and shipping. Manual workflows are prone to delays, errors, and inefficiencies — issues that automation eliminates by replacing paper-based processes with real-time, technology-driven systems.
Organizations that strategically adopt Automating Warehouse Management Workflows often see:
- Faster order fulfillment and improved service levels
- Greater inventory accuracy and real-time tracking
- Reduced labor costs and human errors
- Scalable operations that adapt to growth and peak demand
Key Steps to Automating Warehouse Management Workflows
1. Start with Process Mapping
Before implementing automation, map your current warehouse management workflow to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies:
- Where do delays occur most often?
- Which tasks consume the most time or resources?
- Are there duplicate or unnecessary steps?
This upfront assessment ensures your automation efforts focus on high-impact areas.
2. Implement Automated Inventory Management
Inventory accuracy is critical for any successful warehouse management workflow. Automated systems using barcode scanning, RFID tracking, and real-time updates help eliminate manual errors and improve visibility.
Best practices include:
- Real-time inventory tracking
- Automated cycle counting
- Intelligent slotting based on demand patterns
- Dynamic reorder triggers
3. Optimize Order Fulfillment
Order fulfillment is one of the most labor-intensive parts of the warehouse. The right automation enhances speed and accuracy in your warehouse management workflow by:
- Automating wave picking and efficient route planning
- Enabling voice-directed picking
- Integrating automated packing stations
- Including quality control scans before shipment
These enhancements reduce travel time, errors, and fulfillment costs.
4. Leverage Data Integration & APIs
A fully automated warehouse management workflow depends on seamless data exchange:
- Connect your WMS with ERP, ecommerce platforms, and transportation systems
- Use APIs to synchronize orders, inventory counts, and shipment data
- Break down silos to streamline operations
This connectivity allows for real-time insights and automated triggers, improving responsiveness and accuracy.
5. Use Intelligent Workflow Automation
Beyond basic automation, intelligent systems dynamically adapt workflows based on real-time conditions:
- AI-driven task assignment
- Automated exception handling
- Predictive maintenance
- Adaptive rules during peak demand
These smart features keep your warehouse management workflow flexible and responsive to changing conditions.
Measuring Success After Automating Warehouse Management Workflows
To ensure your automation investment delivers value, track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as:
- Order fulfillment cycle time
- Inventory accuracy rates
- Labor efficiency (orders per hour)
- System uptime and integration error rates
- Customer satisfaction metrics
Monitoring these metrics regularly allows continuous improvement and helps you benchmark progress.
strategies.
Understanding Warehouse Barcode Systems: Foundation of Modern Workflows
Before automating complex warehouse workflows, you need accurate data capture. Warehouse barcode scanning provides the foundation for every automated workflow by creating digital records of physical inventory movements.
What is a Warehouse Barcode System?
A warehouse barcode system assigns unique identifiers to inventory items, storage locations, and equipment, enabling automatic tracking through digital scanning rather than manual data entry. When warehouse staff scan these barcodes using handheld devices, your warehouse management system updates automatically with real-time location and quantity data.
According to research on barcode technology, warehouse barcode scanning eliminates 99%+ of manual data entry errors, provides instant inventory visibility across facilities, enables real-time tracking of product movements, supports automated reordering and cycle counting, and creates complete audit trails for compliance requirements.
Types of Warehouse Barcodes
Different warehousing scenarios require different barcode approaches:
1D Linear Barcodes (Traditional Barcodes)
These familiar horizontal bars work well for basic inventory tracking. Common formats include Code 128, Code 39, and UPC/EAN for retail products. 1D warehouse barcodes store limited information but scan reliably even with older equipment and work on small label spaces.
2D Matrix Barcodes (QR Codes & Data Matrix)
2D warehouse barcodes store significantly more data in smaller spaces. A single QR code can contain product details, lot numbers, expiration dates, serial numbers, and handling instructions. Warehouses handling complex products with extensive attributes benefit from 2D barcode systems.
RFID Tags (Radio Frequency Identification)
While technically not visual barcodes, RFID represents the next evolution in automatic identification. RFID enables scanning multiple items simultaneously without line-of-sight requirements, reading through packaging and containers, longer read ranges than traditional barcodes, and automated inventory verification without manual scanning.
A New Jersey pharmaceutical distributor implemented comprehensive warehouse barcode scanning across all inventory locations and equipment. Before barcode implementation, inventory accuracy hovered at 87% with frequent picking errors. After deployment, accuracy improved to 99.2% and picking errors decreased 73%.
The lesson: Accurate data capture through warehouse barcode systems precedes successful workflow automation.
Implementing Warehouse Barcode Scanning in Your Workflows
Successful warehouse barcode scanning requires more than buying scanners and printing labels. Strategic implementation across all warehouse workflows delivers maximum value.
Step 1: Standardize Location Barcoding
Before labeling inventory, create a logical location hierarchy for your warehouse. Use consistent naming conventions:
Aisle-Bay-Shelf-Bin formats like A1-B3-S2-01. Zone-Row-Position formats like Z1-R15-P08. Warehouse-Zone-Location for multi-facility operations.
Print durable warehouse location barcodes for every storage position. When putaway staff scan location barcodes during storage, your WMS records exact placement automatically, enabling perfect picking accuracy.
Step 2: Choose Scanning Hardware for Your Workflows
Match devices to workflow requirements:
Stationary scanners for receiving and shipping stations where products come to fixed positions.
Handheld scanners give picking and putaway staff mobility throughout the warehouse.
Wearable ring scanners enable hands-free scanning during physical handling, ideal for picking workflows.
Voice-directed systems with barcode verification combine hands-free guidance with scan verification for maximum accuracy.
A Michigan food distributor equipped order pickers with ring scanners integrated to voice-directed picking systems. This warehouse barcode scanning combination improved pick rates 40% while maintaining 99.7% accuracy.
Our enterprise software development capabilities include building custom barcode integration that connects scanning hardware with your specific WMS and workflow requirements.
Step 3: Integrate Barcode Workflows Across All Processes
Warehouse barcode scanning generates valuable data that multiple systems and workflows need:
Receiving workflows scan inbound products to verify against purchase orders and create inventory records.
Putaway workflows scan products and locations to record exact storage positions.
Picking workflows scan items during selection to verify accuracy and update inventory.
Packing workflows scan finished orders to confirm contents and generate shipping labels.
Cycle counting workflows scan locations and products to verify inventory accuracy.
Shipping workflows scan packages to confirm carrier assignments and create manifests.
A California third-party logistics provider integrated warehouse barcode data across client ERP systems, generating automatic shipment notifications and inventory updates without manual data export or re-entry.
Step 4: Train Staff on Barcode Workflow Best Practices
Technology only works when people use it correctly. Train warehouse teams to:
Scan every item at every workflow stage to maintain data integrity. Verify scans visually before proceeding to next task. Report damaged or illegible warehouse barcodes immediately. Understand how scanning discipline impacts entire operation. Never manually enter data that should be scanned.
A Pennsylvania automotive parts warehouse discovered that 15% of picking errors occurred when staff manually entered quantities instead of scanning. Reinforcing scan-every-item discipline reduced errors 82%.
Step 5: Monitor Barcode Workflow Performance
Track metrics revealing barcode system effectiveness:
Scan compliance rate: percentage of required scans completed. Scan error rate: invalid or duplicate scans requiring correction. Barcode label quality: damaged or unreadable labels needing replacement. Workflow completion time: process speed with barcode scanning versus manual methods.
Regular monitoring identifies issues before they cascade into operational problems.
Ready to implement warehouse barcode systems that actually improve your workflows? Explore our warehouse automation solutions to discover implementation strategies matched to your facility.
Common Challenges and How to Avoid Them
Even with the best tools, some warehouses struggle when Automating Warehouse Management Workflows due to:
- Automating broken or inefficient processes
- Insufficient testing prior to deployment
- Poor change management and training
- Lock-in with incompatible vendor systems
- Data quality issues amplified by automation
Ensure you invest in training, robust testing, and data cleanup before full automation rollout.
Conclusion: Why Now is the Time to Automate
A modern, efficient warehouse management workflow is no longer optional — it’s a strategic advantage. By Automating Warehouse Management Workflows, businesses can accelerate fulfillment, cut costs, and build resilient, scalable operations designed for today’s competitive landscape.
Whether you’re just starting your automation journey or optimizing mature systems, understanding best practices ensures you maximize ROI and stay ahead of evolving supply chain demands.