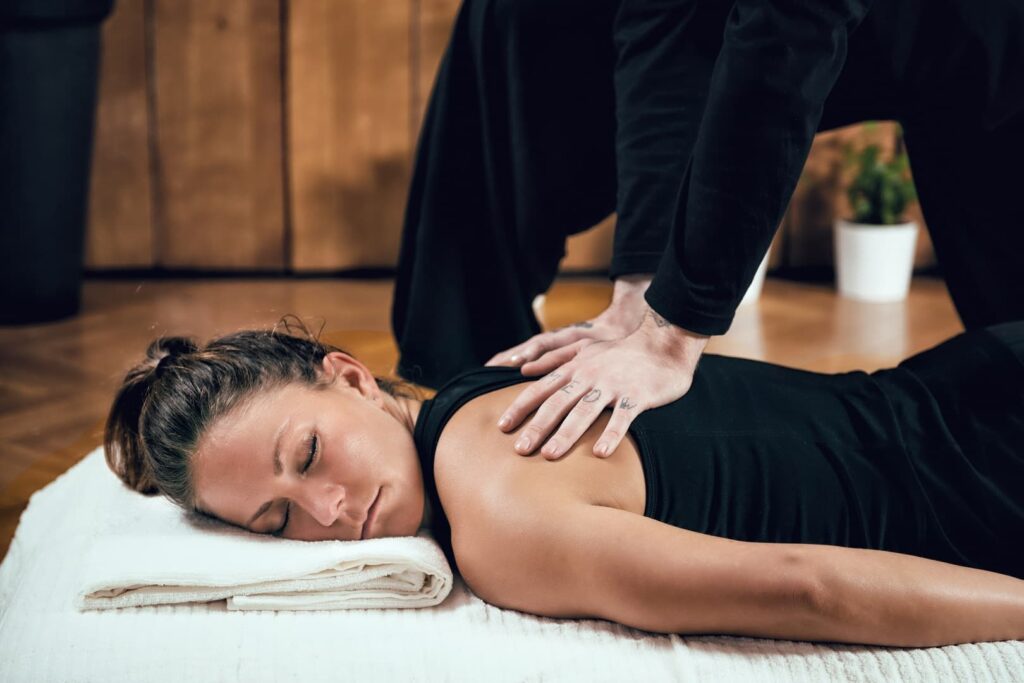
Learning massage techniques requires structured guidance and consistent practice. Enrolling in a Shiatsu Massage Training Course or professional workshop provides a solid foundation in anatomy, pressure points, and relaxation methods. Step-by-step learning allows beginners to build confidence while avoiding common mistakes. Practicing under supervision enhances client safety and develops professional skill. Whether your goal is a career in massage therapy or improving personal wellness skills, following a systematic approach ensures effective technique, greater precision, and long-term competence in delivering professional massage services.
Different Massage Styles
Awareness of various massage styles helps in choosing the right technique for specific needs. Swedish massage promotes relaxation and circulation, while deep tissue focuses on relieving chronic tension. Shiatsu uses finger pressure on acupressure points, and sports massage prepares or rehabilitates athletes. Learning these differences ensures each session is tailored and effective. Practitioners can combine techniques as they advance, enhancing versatility. Understanding styles also aids in targeting specific areas, improving therapeutic outcomes, and meeting client expectations for relief, comfort, and overall wellness.
Essential Anatomy Knowledge
Knowledge of anatomy is vital for safe and effective massage. Understanding muscle groups, joints, and pressure points helps prevent injury and ensures targeted relief. Familiarity with skeletal and circulatory systems improves technique accuracy, body alignment, and posture. Even basic anatomical insight allows precise pressure application and enhances session effectiveness. Anatomy knowledge builds practitioner confidence, ensuring strokes reach areas needing attention. Correct anatomical awareness also strengthens professional credibility, fosters client trust, and supports long-term career development while delivering safe and efficient massage therapy.
Step-by-Step Learning Process
A structured learning path ensures steady progress. Start with theory, covering anatomy, massage principles, and safety practices. Move to basic strokes such as effleurage, petrissage, and friction, mastering them individually. Gradually progress to combining strokes and focusing on specific body regions. Supervised sessions provide feedback and correct errors early. Repetition strengthens muscle memory, rhythm, and pressure control. Step-by-step learning ensures each skill is secure before moving on, allowing beginners to gain confidence and competence while maintaining client safety and session effectiveness at every stage.
Practical Techniques to Master
Foundational techniques form the core of massage proficiency:
- Effleurage: Gentle gliding strokes for relaxation
- Petrissage: Kneading muscles to relieve tension
- Tapotement: Rhythmic tapping to stimulate circulation
- Friction: Deep circular movements to release tight muscles
- Compression: Steady pressure to improve blood flow
Regular practice strengthens hand coordination, pressure accuracy, and smooth stroke transitions. Mastering these techniques builds confidence, prepares practitioners for advanced styles, and ensures each session delivers therapeutic results while maintaining client comfort and safety.
Importance of Posture and Body Mechanics
Proper posture and body mechanics prevent fatigue and injury while improving control over massage techniques. Using body weight instead of only arm strength reduces strain and enhances precision. Standing or seated positions should allow fluid, comfortable movement. Maintaining correct posture ensures energy conservation, sustained pressure, and smooth stroke application. Good mechanics also convey professionalism, building client confidence. Consistently observing body alignment safeguards the practitioner’s health and supports long-term career sustainability while allowing sessions to remain effective, controlled, and comfortable for both client and therapist.
Observation and Learning from Experts
Observing experienced therapists provides insight into advanced techniques, hand placement, and pressure adjustment. Shadowing professionals or attending workshops allows learners to see how methods are adapted for different clients. Watching experts improves timing, rhythm, and responsiveness, which can be difficult to develop alone. Observation also highlights practical tips, client interaction skills, and session flow. Learning from experts helps beginners internalize subtle nuances, refine technique, and enhance confidence. Exposure to professional approaches accelerates skill acquisition while providing a realistic understanding of effective massage practice and client satisfaction.
Consistent Practice and Feedback
Regular, deliberate practice is key to improvement. Practicing with friends, family, or classmates provides safe hands-on experience. Recording sessions or maintaining notes allows evaluation of strengths and weaknesses. Feedback from instructors or clients guides refinement, ensuring mistakes are corrected early. Repetition builds fluidity, pressure control, and instinctive responses. Consistent practice also reinforces confidence and strengthens technique, turning theoretical knowledge into practical skill. Constructive criticism allows targeted improvement, supporting growth toward proficiency while maintaining safe, effective, and professional massage delivery.
Utilizing Learning Resources
Books, online tutorials, video demonstrations, and professional courses supplement hands-on practice. Certification programs provide structured lessons, guidance, and feedback. Apps allow flexible, self-paced learning. Using multiple resources ensures a comprehensive understanding of anatomy, strokes, and techniques. Combining study and practical sessions strengthens skill development, reinforces theoretical knowledge, and enhances confidence before working with real clients. Effective use of learning tools accelerates growth, improves technique accuracy, and prepares practitioners for professional standards in massage therapy while ensuring safe and efficient practice.
Setting Goals and Tracking Progress
Setting clear, achievable goals drives steady skill advancement. Targets may include mastering core strokes, completing full-body massages, or improving pressure control. Tracking progress through notes, videos, or client feedback identifies strengths and areas needing improvement. Breaking skills into smaller milestones maintains motivation and clarity. Monitoring growth builds a roadmap from beginner to proficient practitioner. Goal-oriented practice encourages intentional learning, focus, and measurable development. Clear objectives also help maintain consistency, increase confidence, and provide a structured pathway to mastering massage techniques effectively.
Practicing Self-Care as a Practitioner
Self-care is essential to maintain energy and prevent fatigue. Stretching, proper hydration, and adequate rest reduce the risk of strain and injury. Mindfulness or relaxation techniques improve focus during sessions. Personal wellness allows practitioners to deliver consistent pressure and maintain session quality. Prioritizing self-care ensures long-term sustainability in massage practice while modeling healthy habits to clients. Maintaining fitness and mental clarity enhances skill execution, supports professional performance, and ensures high-quality, safe, and comfortable massage experiences for clients.
Conclusion
Learning massage techniques effectively requires structured guidance, consistent practice, and proper self-care. Mastering foundational strokes, understanding anatomy, observing experts, and applying feedback ensures safe, precise, and effective sessions. Step-by-step progression, combined with goal tracking and use of learning resources, accelerates skill acquisition. Correct posture, body mechanics, and self-care sustain long-term practice. Following this systematic approach enables beginners to develop confidence, competence, and professionalism while offering high-quality massage services across multiple techniques and client needs.
FAQs
1. How long does it take to learn massage techniques effectively?
Consistent practice over several months, combined with formal training, builds mastery in foundational strokes and professional competence.
2. Do beginners need certification to practice massage?
Certification is recommended to ensure safe techniques, anatomy knowledge, and professional standards are met for client safety.
3. Which massage techniques should beginners focus on first?
Effleurage, petrissage, tapotement, friction, and compression are core techniques that form the basis for all massage styles.
4. How does observing experts improve skills?
Observation provides insight into timing, hand placement, pressure adjustments, and client response, accelerating skill development.
5. Why is self-care important for massage practitioners?
Maintaining physical and mental wellness prevents fatigue, supports precision, and ensures consistent, high-quality sessions.